Do Sleep and Exercise Help School Performance?
Overview:
This R project analyzes whether students who sleep more or exercise regularly perform better academically.
The analysis uses a dataset of 10,000 student records, exploring how sleep duration and exercise frequency relate to academic performance.
Data Overview
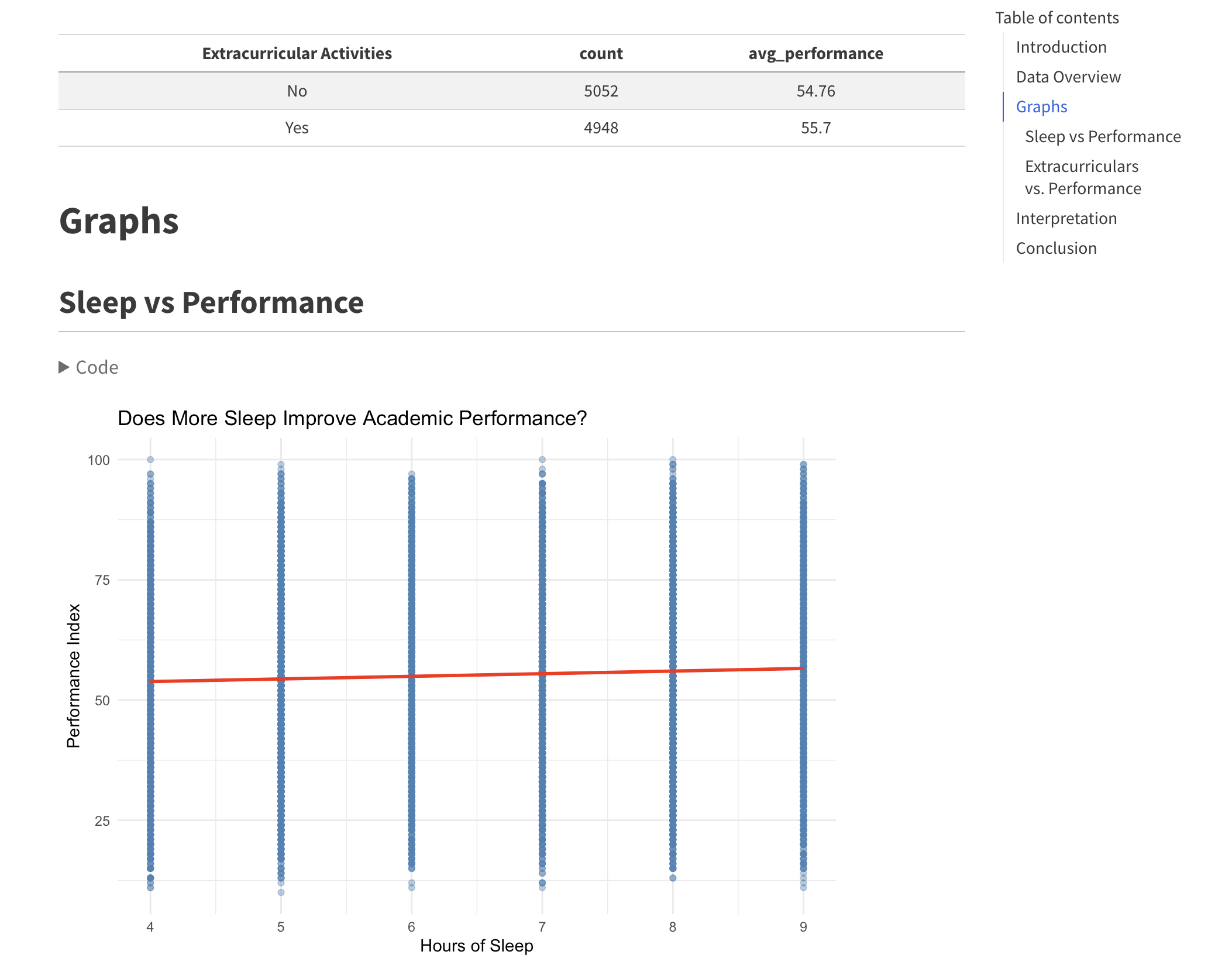
This graph shows how average performance scores vary across different sleep durations.
Results
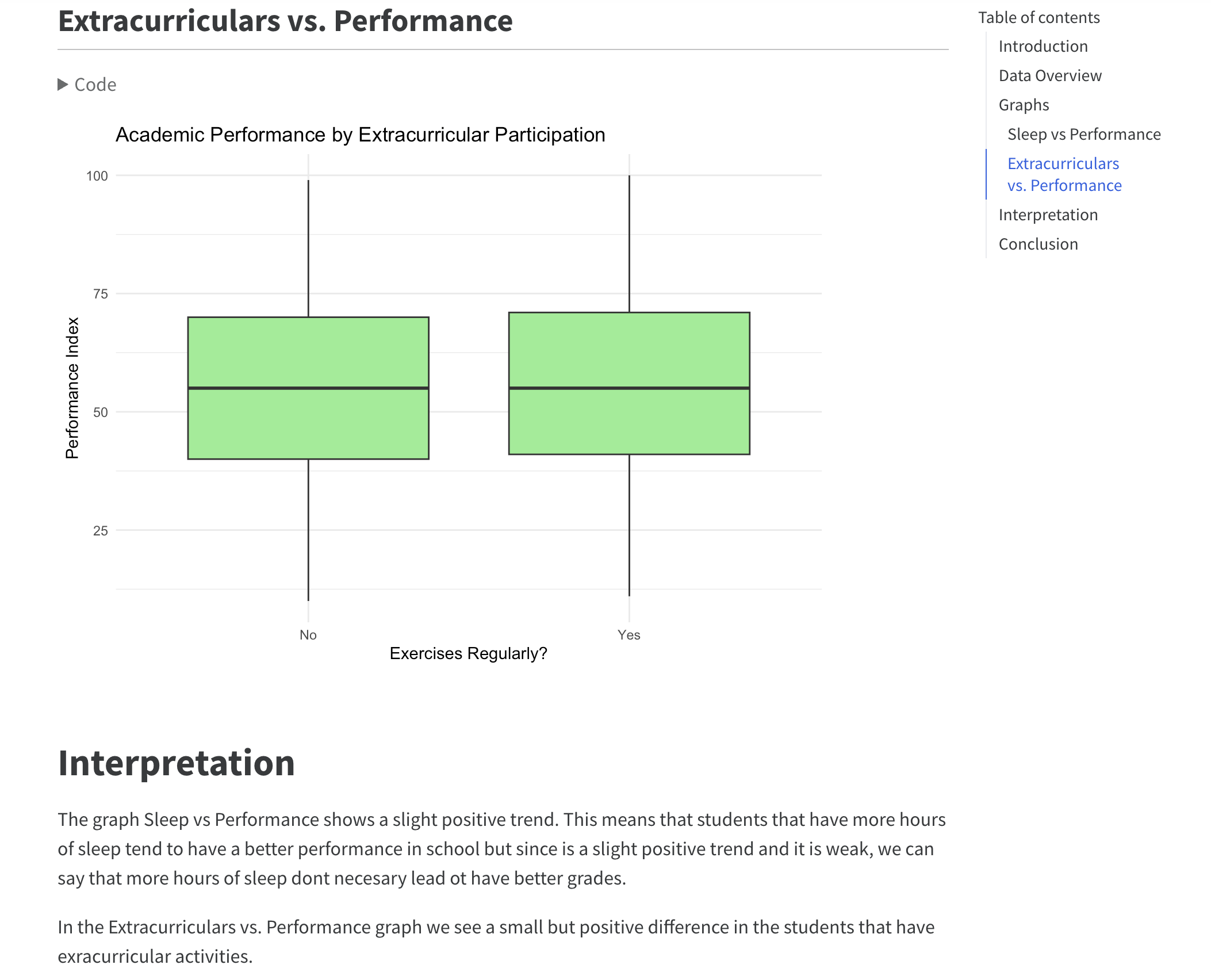
Students who sleep between 7–9 hours and exercise consistently tend to have higher academic scores.
Conclusion

Students with better sleep habits and regular exercise show improved academic outcomes.
While correlation doesn’t prove causation, these findings suggest healthy habits contribute to school success.
Tools used: R, ggplot2, tidyverse, Quarto
Note: The full interactive version is available on BYU–Idaho’s Shiny server (login required).